Linux Kernel 6.13 has recently been released, introducing several new features, including lazy preemption support, user-space shadow stack support for AArch64, and improved virtual machine capabilities under the Arm Confidential Compute Architecture. Ubuntu users are now able to install this latest kernel via the official Mainline Kernel PPA archive, whether they need additional hardware support or want to explore the new features.
This tutorial assumes testing on Ubuntu 24.10 and confirms a smooth installation process. Users can find kernel packages available for various architectures, including 64-bit (x86_64), AArch64 (ARM64), and others. However, it is essential to note that the Ubuntu Kernel Team does not support these kernels and will not be accountable for any installation-related issues or damages.
Method 1: Using the Mainline Kernels Tool
The simplest way to install Linux kernel 6.13 is through the graphical tool called Mainline Kernels. To install this tool, open the Terminal and run:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:cappelikan/ppasudo apt update && sudo apt full-upgradesudo apt install -y mainlineAfter installation, launch the Mainline Kernels tool from the applications menu. The tool will check for available kernel versions from Canonical’s Mainline Kernel PPA archive. Click on the latest kernel version and hit “Install.” Once the process is complete, reboot your system. This tool also keeps you informed about new kernel updates if notifications are enabled.
Method 2: Command Line Installation
For more experienced users, the command line method offers a fallback for those who prefer not to utilize the graphical tool. You can manually download and install the kernel packages for your architecture from the official Ubuntu mainline kernel PPA archive.
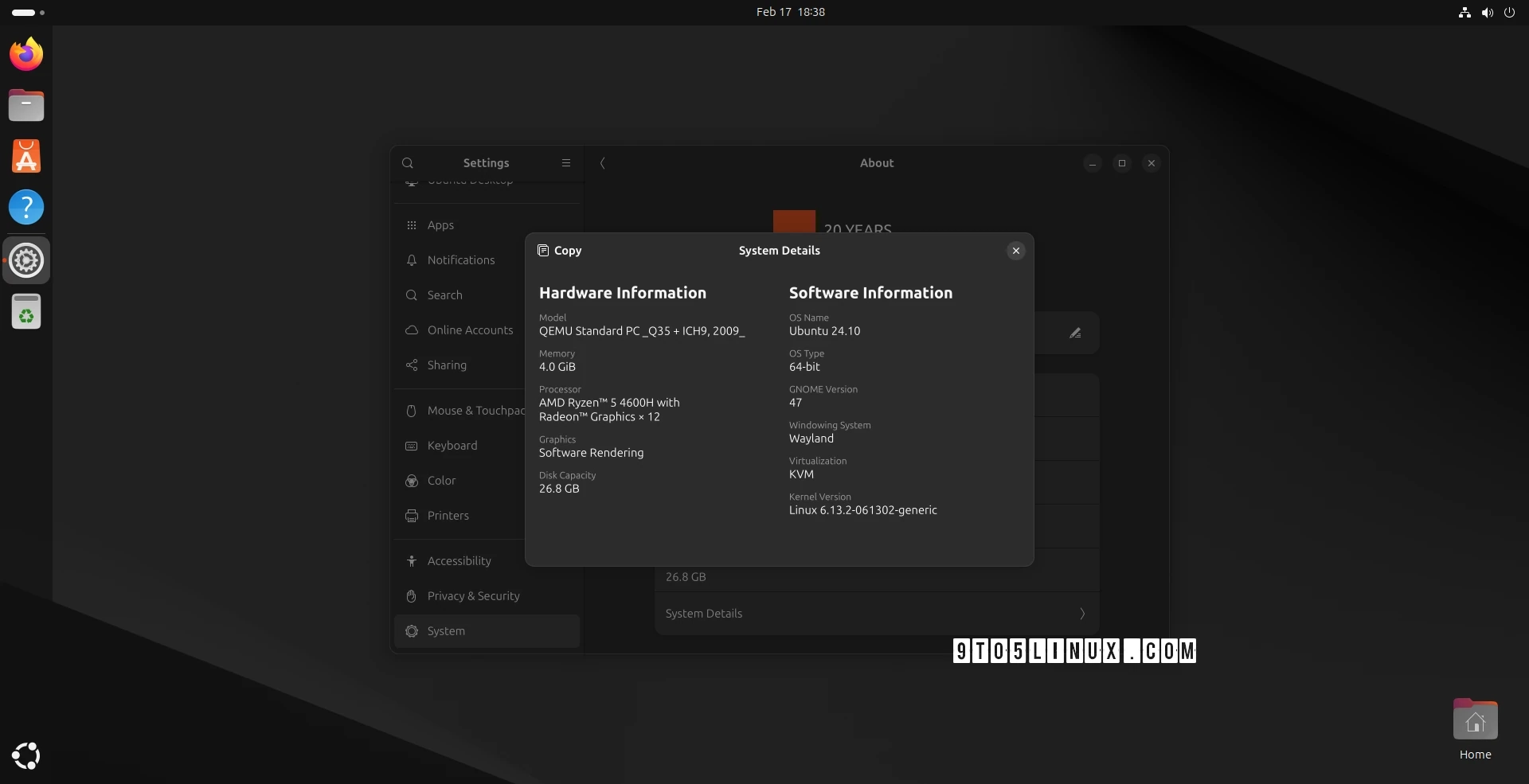
Here’s how to install Linux kernel 6.13.2 on a 64-bit system:
-
Download the necessary kernel packages:
-
After downloading, navigate to the folder containing the packages and run:
sudo dpkg -i *.debReverting to a Previous Kernel
Should any issues arise with the new kernel, you can revert to the default or any previously installed kernel. During boot, press the Esc key to access the boot menu. Then, select “Advanced options” to choose an alternate kernel version.
For more details and steps, please refer to the links provided for the Linux Kernel 6.13 release and related topics.